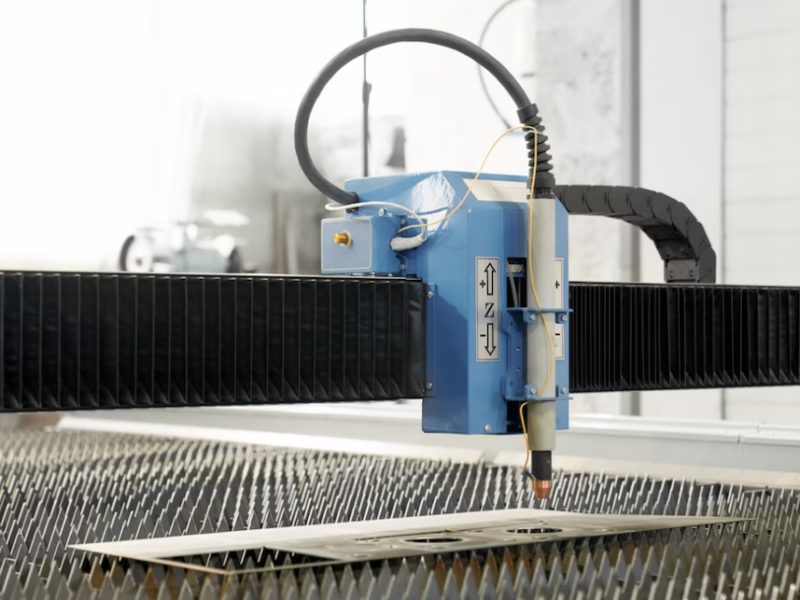
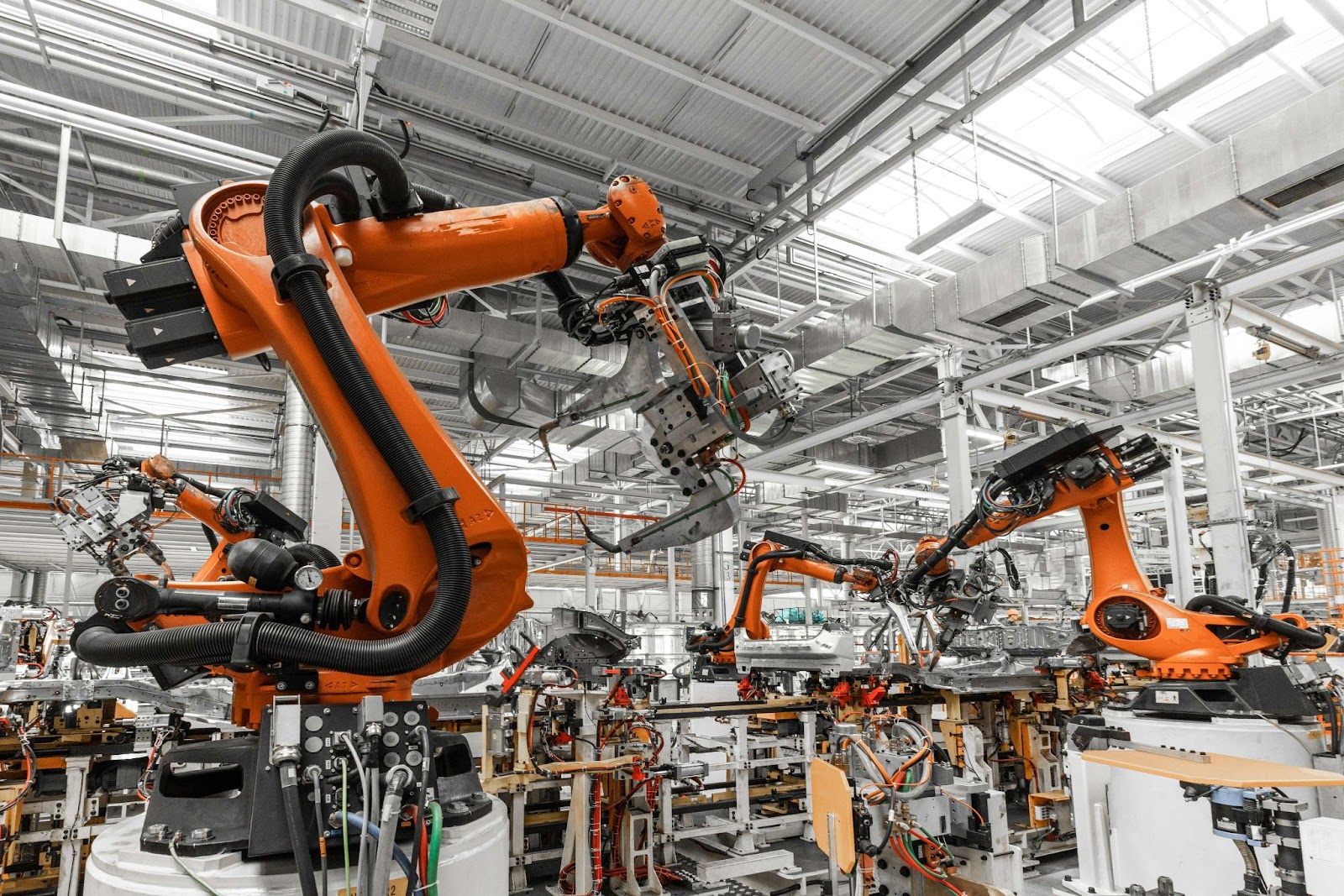
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized the manufacturing industry with their precision, efficiency, and versatility. From small workshops to large-scale production facilities, automated machines have become essential tools for various applications, including milling, turning, routing, and more. However, one crucial question remains for businesses and individuals alike: How much do these advanced machines cost? In this article, we will delve into the factors that influence their prices and explore different options for various budgets, helping you make an informed investment decision.
What is CNC Machine?
CNC, an abbreviation for computer numerical control, is a revolutionary manufacturing process that harnesses the potential of software to command various types of CNC machines. This cutting-edge technology enables skilled machinists and operators to produce precise parts by utilizing mechanical design, drawings, mathematics, and computer programming skills. For instance, CNC programmers can take a metal workpiece and craft essential aerospace or automotive components with exceptional accuracy. Modern CNC machines often integrate multiple tools, streamlining the entire machining process for enhanced efficiency.
The Role of CNC in Machine Control
The primary role of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) is to govern the movements of a machine tool with precision and automation. By combining digitized data, a computer, and a computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) program, CNC technology efficiently controls, automates, and monitors the motions of CNC tools. In large industrial machines, an integrated computer serves as a dedicated onboard controller, while smaller hobbyist models rely on an external computer.
Every CNC controller collaborates with multiple motors and drive components to execute and manage the programmed motions. Sophisticated machines further enhance their precision with a feedback system that continuously monitors and adjusts the cutter’s speed, feed rate, and position during operations.
Key Factors of CNC Machine Pricing
The cost of CNC machines can vary significantly depending on several key factors. Let’s explore these factors to gain a clearer understanding of the price range and options available.
- Machine Type: The type of CNC machine you choose, such as milling machines, lathes, or plasma cutters, will significantly impact the overall cost. Specialized machines tailored for specific applications may also come at a premium;
- Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of a CNC machine determine the maximum workpiece size it can accommodate and the complexity of the projects it can handle. Larger and high-capacity machines generally command higher prices;
- Brand and Quality: Reputable brands and machines with superior build quality and performance tend to have higher price tags. While these machines may require a larger upfront investment, they often offer better reliability and longevity;
- Features and Functionality: CNC machines can come equipped with various features and add-ons, such as automatic tool changers, coolant systems, and advanced control interfaces. Each additional feature contributes to the overall cost;
- Automation and Technology: The level of automation and technological advancements integrated into a CNC machine can affect its price. More advanced automation can increase productivity and efficiency but may also come with a higher cost;
- New vs. Used: Purchasing a new CNC machine comes with the advantage of warranties and the latest technology, but it also tends to be more expensive. Opting for a well-maintained used CNC machine can offer significant cost savings without compromising performance.
Types of CNC Machine Tools and Their Applications

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools have revolutionized modern manufacturing, enabling precision, efficiency, and versatility in various industries. Here are some examples of CNC machine tools:
- CNC Milling Machines: These machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece to create complex shapes and designs. CNC milling machines are widely used in automotive, aerospace, and prototyping industries;
- CNC Lathe Machine: A CNC lathe machine rotates the workpiece while cutting tools are applied to shape it. This process is ideal for producing cylindrical components like shafts, bolts, and fittings with high precision;
- CNC Wire Electric Discharge Machine (EDM): This CNC machine tool uses electrical discharges to erode material from a workpiece, producing intricate shapes and patterns. EDM is commonly used for toolmaking and mold manufacturing;
- CNC Grinders: CNC grinders use abrasive wheels to precisely grind and finish surfaces on various materials, including metals and ceramics. They are crucial for achieving tight tolerances and high-quality surface finishes;
- CNC Laser Cutters: These machines utilize a powerful laser beam to cut through materials such as metal, wood, and acrylic with incredible accuracy. CNC laser cutters find applications in signage, jewelry making, and sheet metal fabrication;
- CNC Plasma Cutters: Similar to laser cutters, CNC plasma cutters use a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials like steel, aluminum, and copper. They are commonly used in metal fabrication industries;
- CNC Waterjets: CNC waterjets utilize a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through various materials, including stone, glass, and composites. They are known for their ability to cut intricate shapes without creating heat-affected zones;
- CNC Routers: CNC routers use rotating cutting tools to hollow out or shape materials such as wood, plastic, and foam. They are extensively used in woodworking, sign making, and prototyping;
- 3D Printers: In a Class by Themselves: While not traditional subtractive CNC machines, 3D printers use additive manufacturing techniques to build objects layer by layer from digital models. They have gained immense popularity in various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, and automotive, for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing.
Analyzing CNC Machine Costs Across Categories
| CNC Machine Category | Cost |
|---|---|
| Entry-level desktop CNC routers | $150-$500 |
| Hobby-level CNC router | $1,000-$3,000 |
| Hobby-level CO2 laser | $1,000-$3,000 |
| Hobby/Small Business plasma table | $1,000-$5,000 |
| Professional CNC Machine | $50,000-$100,000 |
| Entry-Level 3-axis Mill | $50,000-$100,000 |
| Industrial HD plasma tables | $40,000-$120,000 |
| Industrial Fiber Laser | $100,000 – over $500,000 |
| Production 3-axis CNC Milling Machines | $100,000-$500,000 |
| Production 5-axis CNC Milling Machines | Over $500,000 |
Other Expenses Linked to CNC Machines
In tandem with the factors mentioned earlier, there are sundry tools, accessories, and licenses that could entail additional expenses in CNC processes. The necessary tools might encompass lubricants and coolants, twist drills, a milling vise, as well as inspection and measuring tools, depending on the specific machine.
Moreover, one must take into account the cost of hiring machine operators, material procurement, storage expenses, and maintenance requirements. All these supplementary costs could range from several hundred to thousands of dollars, contingent upon the scale of your operation.
Key Considerations Before Investing in a CNC Machine
Investing in a CNC machine can significantly enhance your manufacturing capabilities, but it’s crucial to make an informed decision before making the purchase. Here are five essential factors to consider:
- Specific Requirements:
Evaluate the nature of your work and the materials you’ll be working with. Understanding your needs will guide you in selecting the right machine size, power, and type that aligns with your production demands;
- Available Space:
Assess the space you have available for the CNC machine, including the required footprint and additional room for accessories and material storage. Proper spatial planning ensures smooth operations and avoids unnecessary constraints;
- Budget and Total Cost of Ownership:
Determining your budget is vital, but remember to account for the total cost of ownership. Consider not only the initial investment but also installation, necessary accessories, operational expenses, and maintenance costs throughout the machine’s lifecycle;
- Technical Requirements:
Before finalizing your purchase, thoroughly evaluate the technical aspects. Ensure that your workspace can accommodate the machine’s power supply and ventilation needs, and check if any infrastructure modifications are necessary;
- Software Compatibility and Training:
Assess the software requirements of the CNC machine and verify compatibility with your existing software and hardware. Additionally, consider the ease of use of the machine’s software and the need for any training to maximize its potential;
- Bonus Tip: Outsourcing as an Option
For individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, outsourcing CNC machining needs to specialized manufacturers might be a financially prudent decision. Partnering with reputable service providers can help you avoid the substantial upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs associated with owning a CNC machine.
By carefully considering these factors, you’ll be better equipped to select the right CNC machine solution that aligns with your production goals and optimizes your manufacturing processes.
Purchasing Pre-Owned Machines

Another cost-saving option when acquiring a CNC machine is to consider buying used equipment. While the market mainly caters to machines valued at $10,000 or higher, opting for pre-owned machinery can lead to substantial savings. The amount you can save varies significantly, ranging from several thousand to several hundred thousand dollars, contingent upon the specific type of machine you are interested in.
Websites such as MachineTools provide an excellent platform for both buying and selling used machinery, offering valuable insights into potential cost savings for your purchase.
If you opt for a used CNC machine, conducting thorough due diligence during the inspection process is crucial. Pay attention to various aspects, such as noise levels during operation, the machine’s CNC usage time, stored alarms, alarm history, maintenance records, and any signs of leaks or issues.
Two Examples of Top-Shelf CNC Machines
Presenting two top-shelf examples of CNC machines that exemplify the combination of modern computer technology and quality engineering:
CNC Masters Supra Vertical Knee Mill:
The CNC Masters Supra Vertical Knee Mill stands as a testament to exceptional craftsmanship, setting it apart from average CNC machines. Designed in the USA, specifically in Irwindale, California, this Bridgeport-type CNC knee mill embodies excellence and practicality. Its range of table sizes caters to different needs, making it accessible even to small shops and hobbyists. Boasting a host of helpful features, the Supra is a versatile CNC milling machine suitable for a variety of applications, including production work, product development, rapid prototyping, engraving, and educational purposes in institutions like community colleges, vocational schools, and science labs. With user-friendly controls and software, operators can quickly grasp its functionality, enabling them to fabricate both simple and intricate parts with ease and precision, making it a valuable asset for any workshop.
1440 CNC Lathe Machine:
The 1440 CNC Lathe Machine is a prime example of outstanding CNC engineering, delivering a solution for high-volume round work that surpasses expectations. No longer reliant on expensive outsourcing to large shops, this CNC lathe transforms complex manual turning tasks into simplified programming language. With its ability to accurately execute intricate parts during production runs, businesses can optimize their efficiency and productivity. Moreover, when dealing with one-off pieces, the 1440 CNC Lathe seamlessly transitions to manual control, eliminating the need to create a CNC program for short production runs. This combination of automated precision and manual flexibility makes the 1440 CNC Lathe an ideal choice for manufacturers seeking cost-effective solutions and impeccable results.
Conclusion
The pricing of these advanced automated machines can vary significantly, with more basic models being relatively budget-friendly and suitable for small-scale operations or hobbyists. On the other hand, the top-of-the-line industrial variants can carry a substantial price tag. It remains crucial for potential purchasers to thoroughly evaluate their specific requirements, production needs, and financial limitations before committing to such equipment. The long-term advantages of enhanced efficiency and precision that these machines offer make them a worthwhile investment for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge in today’s manufacturing landscape. With diligent research and exploration of available alternatives, both individuals and companies can discover the perfect machine that aligns with their objectives, ensuring maximum return on their investment in the manufacturing process.